Russian Researchers Assessed the Likelihood of Sleep Disorders after COVID-19
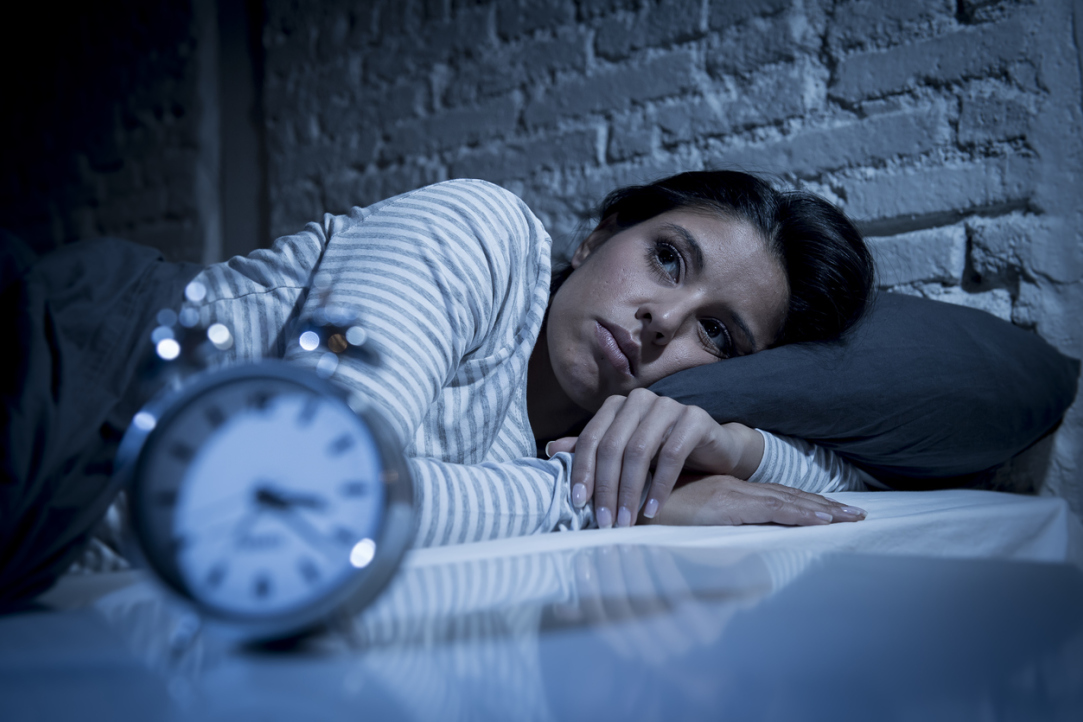

A team of researchers from the HSE Centre for Cognition and Decision Making and the Central State Medical Academy conducted a study on sleep disorders, mood and fatigue after COVID-19. These factors are interrelated and the researchers recommend a comprehensive approach to treat the problem effectively. The work was published in the journal Neuroscience and Behavioral Psychology.
Several factors complicate efforts of studying mental health during an epidemic. First, the use of different questionnaires can distort the results and, second, the results can be interpreted in different ways. Additional difficulties in examining patients and conducting the research during the epidemic can also arise. Doctors and researchers have difficulty conducting their study if the patient is in quarantine and cannot receive assistance due to stress from prolonged isolation and a weakened state caused by the virus itself. Therefore, doctors and researchers use telemedicine technologies more often to communicate remotely with patients. Coupled with the appropriate hospital equipment, it becomes possible to conduct psychiatric and psychological examinations that do not require a physical presence. Such measures create conditions under which the doctor can provide assistance without entering the ‘red zone’, in a manner that is comfortable for both the physician and the patient.
The study involved 119 hospitalised patients with confirmed COVID-19 diagnoses who completed four questionnaires for depression, anxiety, fatigue and sleep disorders. Patients with higher than average scores in the results of questionnaires also underwent psychiatric interviews.
The survey found high levels of mood disturbances and sleep disorders among study participants. In all, 28% of respondents reported a decline in mood, 27% experienced a disruption in the quality of their sleep, and 73% suffered from fatigue. Higher levels of fatigue increased the risk of anxiety and depression. Likewise, increased anxiety and a decline in mood also affected overall vitality.
Such results indicate that depression can make people who have recovered from COVID-19 feel less vigorous in their daily lives. Doctors often attribute patients’ rapid loss of energy to the organic consequences of the infection, losing sight of the anxiety and mood disorders that can be masked by the infectious disease. Such an approach can result in a protracted course of asthenia during recovery from the illness, despite favourable physiological parameters. The results also showed that increased anxiety and depression have an effect on the quality of sleep.

Ainur Ragimova, Research Fellow at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience
‘Although the relationship between mood and sleep disorders is intuitive, it is important to examine them carefully and separately especially in patients after COVID infection. Oddly enough, this aspect is often overlooked in the clinical examination of patients with COVID-19. Their sleep problems are more often attributed to physiological disturbances such as the consequences of a stay in intensive care and the effects of a prolonged lack of movement, but not to mood disorders. Our data once again underscores that when patients complain of sleep problems, it is necessary to screen their mental state both during their illness and after their quarantine has ended.’
Foreign studies have looked at the high prevalence of mood and sleep disorders in coronavirus patients during the current and past epidemics. For example, according to Italian studies, anxiety levels have increased from 5% to 36% and sleep disorders from 27.6% to 51.2% during the current epidemic.
The data obtained support theories about the relationship between sleep disorders, mood and fatigue. One of these aspects is often missed during patient exams. For example, when a patient complains of mood disorders, the doctor might fail to ask if the patient also experiences sleep disorders, and vice versa.
It is no easy task to treat mood disturbances, increased anxiety and impaired sleep quality in COVID-19 patients during their illness and recovery. First of all, the authors note, the drugs prescribed should be compatible with physiological indicators and test results (functions of the lungs, liver, kidneys and cardiovascular system) and should be checked for cross-interactions with the main drug treatment. The authors recommend prescribing low doses of non-benzodiazepine anxiolytics (benzodiazepine tranquilizers can adversely affect weakened respiratory systems) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. The prescribed treatment must be monitored by a doctor and the prescribed doses should be carefully tested and titrated.
‘The current pandemic has not only changed the world in social terms, but has also affected the pattern of mental illness in the population’, commented Ainur Ragimova. ‘We are now seeing an increase in neuropsychiatric disorders of varying severity. The results of this open study indicate that COVID-19 has a significant influence on the formation of anxiety-depressive symptoms and sleep disorders’, she said.
Ainur Ragimova
Research Fellow, Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience
See also:
Cognitive Reappraisal of Negative Emotions Can Help Manage Stress
Researchers at the HSE International Laboratory of Social Neurobiology assessed the effectiveness of two strategies for regulating emotions: reappraisal and suppression. Having analysed data on the electrical activity of 60 individuals’ brains, the scientists discovered that both approaches put additional strain on the nervous system. It was also found that individuals who are prone to emotional contagion tend to be more effective in using reappraisal and managing negative emotions. The paper has been published in Experimental Brain Research.
Russian Researchers Unveil Mechanism Underlying Language Processing Disruptions in Epilepsy Patients
Researchers at HSE University and the Pirogov National Medical and Surgical Centre have examined alterations induced by epilepsy in the language-related neural network within the brain. Using graph-based analysis, the researchers studied fMRI data from 28 patients and found that in epilepsy, both hemispheres of the brain become activated during language processing and short connections form between the hemispheres, while long connections within one hemisphere are disrupted. The study has been published in Epilepsy&Behavior.
Paper by HSE Biologists Included in the Top 5 Popular Articles of PeerJ Journal
An article by researchers from HSE University’s Faculty of Biology and Biotechnology is among the most read articles published in the PeerJ journal in 2023. In the paper, the researchers establish a link between the genetic characteristics of the human immune system and its ability to effectively resist new waves of COVID-19. PeerJ is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering research in the field of biological and medical sciences. Every year the editors compile a ranking of the most popular scientific papers.
HSE Creates ‘Transfer of Neurocognitive Technologies’ Consortium
HSE, the Pirogov National Medical and Surgical Centre, and the Centre for Speech Pathology and Neurorehabilitation of the Moscow Healthcare Department have signed an agreement on cooperation and the creation of a ‘neuro-consortium’ under the name ‘Transfer of Neurocognitive Technologies’. The new body will boost the development and implementation of advanced solutions in neurotechnology aimed at maintaining and improving people's health. The agreement was signed for five years, and the consortium is open to new participants.
'While it May Sound Futuristic, It Holds Great Promise': Olga Dragoy Shares Her Thoughts on Language Function Restoration and the Future of Neurotechnology
In the spring of 2023, the fifth strategic project of the Priority 2030 programme, 'Human Brain Resilience: Neurocognitive Technologies for Adaptation, Learning, Development and Rehabilitation in a Changing Environment,' was launched at HSE University. The strategic project brings together researchers from all campuses of HSE University. In her interview with the HSE News Service, Olga Dragoy, head of the strategic project and Director of the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, shares an overview of the advanced technologies neuroscientists are creating today, the underlying inspiration driving these efforts, and the operational dynamics of interdisciplinary applied projects.
‘It Was Great to Look at Scientific Achievements through the Eyes of a Journalist, not a Scientist’
HSE University in Nizhny recently hosted the 2nd Autumn Neuro-linguistic School ‘NeuroSciCom: Popularising Language and Brain Studies’ for scientists and students at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain Studies in Nizhny Novgorod. The school was held as part of the 'Human Brain Resilience: Neurocognitive Technologies for Adaptation, Learning, Development and Rehabilitation in a Changing Environment' Strategic Project of the Priority 2030 programme.
The Brain Is a Network of Networks. Scientists Have Found a Way to Unravel Them
A team of researchers from HSE University and the Artificial Intelligence Research Institute (AIRI) have demonstrated the effectiveness of the PSIICOS method they had previously developed for non-invasive mapping the neural networks in the brain based on its electrical activity. Unlike other methods, it does not search for individual neuronal sources to be then combined into networks but instead looks directly for the functional networks of interconnected neuronal populations—and does so swiftly and accurately. The study findings have been published in NeuroImage.
HSE Neuroscientists Use Neural Network to Enhance Neurofeedback Technology
Researchers from HSE University and the Artificial Intelligence Research Institute (AIRI) have successfully lowered the latency between a change in brain activity and the presentation of the corresponding neurofeedback signal by a factor of 50. The results were obtained by employing a neural network trained in low-latency filtering of brain activity signals from diverse individuals. This approach opens up new prospects for the treatment of attention deficit disorder and epilepsy. A paper with the study findings has been published in Journal of Neural Engineering.
Online Rhythmic Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Can Reveal the Precise Moment When Preferences Shift in the Human Brain
Cognitive dissonance is a complex and multifaceted psychological phenomenon that arises in challenging decision-making scenarios. Multiple regions of the brain participate in its occurrence, yet the neurodynamics of underlying cognitive mechanisms remain a subject of debate. Researchers from the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have proposed the use of online transcranial magnetic stimulation applied to participants as they were actively engaged in tasks, to pinpoint the moment of cognitive dissonance resolution. Their findings have been published in a review paper in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
HSE University Holds 10th Summer School ‘Eye-tracking in the Lab and Beyond’
This year, more than 100 students from Russia and abroad took part in the 10th summer neurolinguistic school, ‘Eye-tracking in the Lab and Beyond’. The school is held annually by the HSE Center for Language and Brain. Leading experts spoke about advanced developments and research in the field of video-oculography.