HSE University’s Third Satellite Launched from Vostochny Cosmodrome
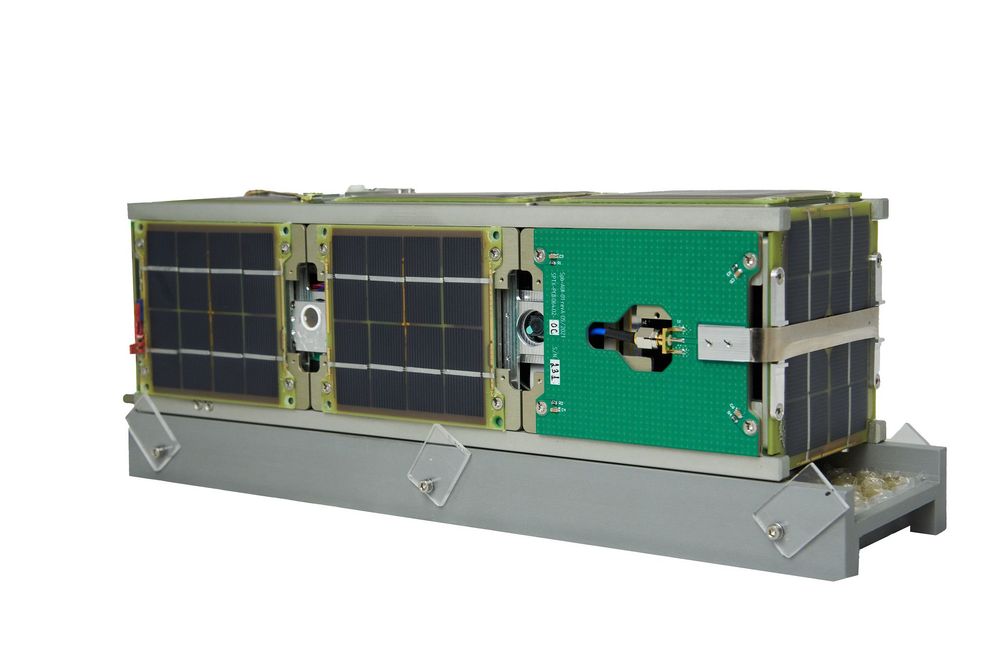
The small CubeSX-HSE-3 spacecraft was created by students and staff of the HSE Tikhonov Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics. It is based on the OrbiCraft-Pro 3U platform by Sputnix. The work was carried out as part of the Space-π project with support from the Innovation Support Fund.
On the morning of June 27, the State Commission at the Vostochny Cosmodrome approved the fuelling of the Soyuz-2.1b carrier rocket and its launch at 2:34 pm Moscow time. The launch vehicle with a Fregat upper stage also took the Meteor-M No. 2-3 satellite into orbit, as well as 42 small spacecraft (3 foreign and 39 Russian, including CubeSX-HSE-3) as a secondary payload. The simultaneous launch of such a large number of Russian satellites—40 in total—set a national cosmonautics record.

The carrier rocket operated as planned; the upper stage separated from the third stage of the rocket, and the spacecraft were placed into their designated orbits.
This was the ninth launch of a Russian carrier rocket in 2023, and the second from the Vostochny Cosmodrome. This was the 63rd flight of the Soyuz-2.1b carrier and the 115th for the Fregat family.
The CubeSX-HSE-3 satellite carries a modified hardware-software AIS complex, an AZN-V monitoring system, and a camera. The CubeSat consists of three units secured on a single frame. One unit houses the flywheels that orient the craft in space, the second contains the boards responsible for the satellite's operation, and the third is entirely allocated to the payload.
The first HSE satellite was launched into space in March 2021, and the second was launched in August 2022.
See also:
HSE University Satellites: Three Years in Orbit
In March 2024, HSE University celebrated an important milestone — the third anniversary of the successful operation in orbit of its first CubeSX-HSE and CubeSX-Sirius-HSE satellites. These spacecraft, created on the basis of the CubeSat platform for Earth observation, continue to function actively, confirming high technological standards and reliability of the university's developments.
‘We Control the Flight of Small Spacecraft’: How HSE University Launches Satellites
Following the meeting with participants of the 3rd Young Scientists Congress, Russian President Vladimir Putin assigned the government to include the creation and launch of small spacecraft in a new national project. Universities will also be involved in the project. Dmitrii Abrameshin, Head of the Mission Control Centre at the Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics at HSE University, spoke about the mechanism of small satellites and which satellites have already been launched by HSE University.
The Path to the Stars: How HSE University Launches Satellites and Gathers Talent
The CubeSX-HSE-3 satellite, created by staff and students of HSE MIEM and based on the OrbiCraft-Pro 3U platform developed by the SPUTNIX private space company, was launched into low-Earth orbit in June. It is the third research vehicle developed at HSE University as part of the SPACE-π project. The HSE University team plans to launch another spacecraft in December 2023 and in the future, it plans to launch two CubeSats into orbit per year. In a special report for the HSE News Service, HSE University’s Project and Educational Laboratory of Economic Journalism explains what HSE University’s satellites do in space and what kind of work goes into them on Earth.
In Space with MIEM: All Systems Go!
On April 12th, the traditional Big Space Break took place at the HSE MIEM. This interactive event for students and staff was organized by specialists from the Laboratory of Space Vehicles and Systems' Functional Safety.
HSE University’s First Satellite Travels 478.7 Million km
The satellite entered orbit two years ago. The launch of the Soyuz-2.1a rocket with a Fregat upper stage and 38 satellites on board, including CubeSX-HSE, took place on March 22, 2021 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome.
Second HSE University Satellite Launched from Baikonur
On August 9, a Soyuz 2.1b rocket launched with a payload of HSE University’s second satellite, which will monitor the land surface of the Arctic region. HSE MIEM Deputy Director Andrey Abrameshin spoke about the university’s space plans, while Top Class competition winner Alexey Gilenko shared his impressions of the launch at Baikonur Cosmodrome.
HSE University Is Preparing to Launch its Second Satellite into Space
Only one year ago, the first HSE University satellite, developed by specialists and students from the Laboratory of Space Vehicles and Systems’ Functional Safety of the HSE Tikhonov Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics (MIEM HSE) and the Sputnix space company, was launched into orbit. And now, the date of the second HSE University’s satellite launch has been announced: Roscosmos will send it into space from Baikonur Cosmodrome on August 9th, 2022.
'Our Work Will Be Useful in the Search for Earth Twins’
Why is space so fascinating? Who is hindered by the Earth's geocorona? What personal qualities are essential for a research physicist, and how will academic careers regain their prestige? These were the questions that came up in HSE News Service’s interview of Igor Balyukin, a Senior Lecturer of the HSE Faculty of Physics and the winner of the 'Best Work Performed by Young Scientists' nomination category of the RAS Space Research Institute competition.
Dust Cloud around the Moon
HSE researchers, together with colleagues from Space Research Institute of RAS, MIPT, and the University of Colorado, ventured to find out where the plasma-dust cloud around the Moon comes from. To do this, they compared theoretical calculations with experimental data and theorized that this cloud likely consists of matter that rose from the Moon’s surface as a result of meteoroid collisions.