Two Worlds of Residents: Car Owners Look at Shared Urban Courtyards Differently from Pedestrians
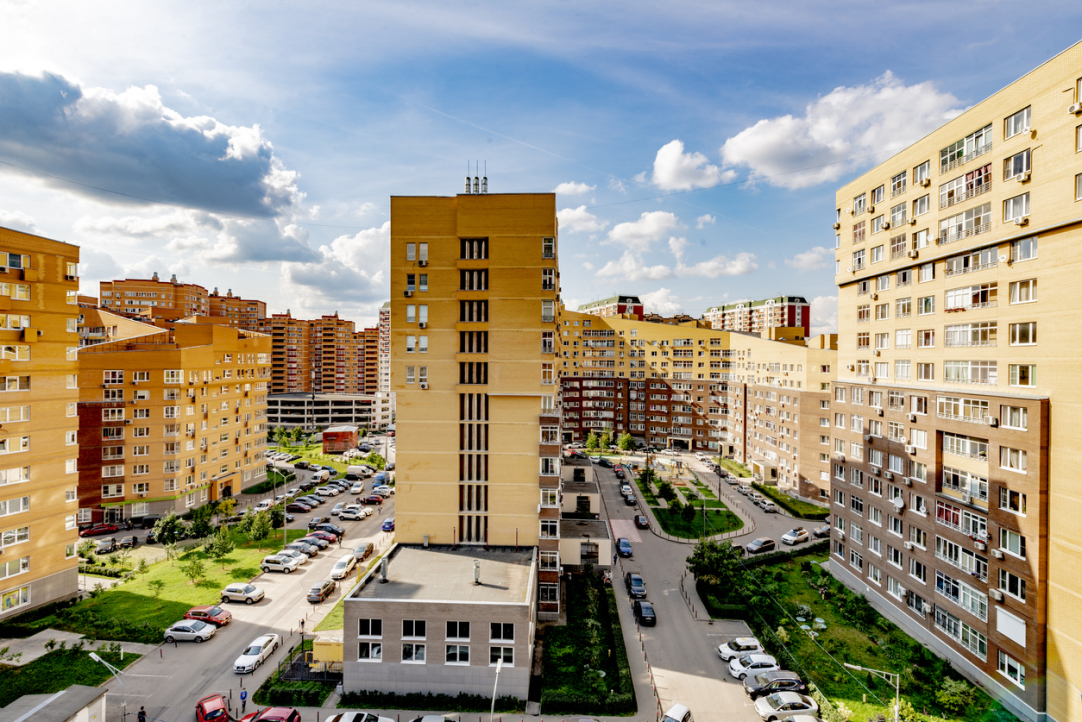

Researchers from HSE University and St. Petersburg State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering (SPSUACE) used eye tracking to study how residents who own cars and those who don’t look at the shared courtyards of multistorey apartment buildings. The study was published in Urban Forestry & Urban Greening.
In many countries, new urban districts are full of lifeless parking lots and there is almost no greenery. And while urban residents like spending time in green parks, they continue to accept the barren courtyards of new housing developments.
The study by HSE University and SPSUACE used eye-tracking technology to study how residents perceive the shared courtyards of apartment buildings.

The researchers took two groups of participants—those who own a car and those who don’t—and showed them images of shared courtyards, asking the subjects to evaluate their attractiveness. A total of 20 car owners and 20 people who did not own a car took part in the study.
The researchers found that the longer people looked at trees (greenery), the more attractive the courtyards seemed to them. And vice versa: the longer they looked at parking lots, the more unattractive they found the area. Computational data analysis confirmed the correlation between the time spent looking at trees and the courtyards’ attractiveness, with an opposite negative effect from looking at parking lots. On average, a twofold increase in attention to greenery makes a courtyard about 30% more attractive.
Car owners found courtyards full of parking spaces and no trees less unappealing than those who don’t own a car. But among car owners, the correlation between the time spent looking at trees and their evaluation of a courtyard as particularly attractive turned out to be the strongest. Greenery impacted car owners 33% stronger than participants without cars.

Vasily Klucharev, the project’s coordinator and Director of the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience
‘The results demonstrate an internal conflict in urban residents who own a car: they are interested in additional parking spaces, but still value greenery highly. Resolving such internal tensions in various groups of urban residents will likely help return cosy green courtyards to our cities.’

Nadezhda Kerimova, co-author of the paper, Associate Professor at the Department of Architectural Design, SPSUACE
‘Architects often underestimate the importance of green spaces during construction planning. Together with an HSE laboratory, we used a contemporary method of eye tracking to study the urban residents’ attention. Our results have confirmed that the more attention people pay to green spaces, the more positively they evaluate urban districts. Such studies are extremely important for changing the philosophy of architects and developers, for understanding the preferences of residents and potential conflicts between different groups of residents.’
‘In our studies, we are trying to get to the bottom of why we accept the concrete of modern construction and forget that green spaces in cities are necessary, first of all, for our health. Trees decrease air pollution, protect us from noise and heat, decrease the chances of cardiological and psychological disorders. Furthermore, Canadian researchers recently proved that having ten more trees in a city block improves health perception in ways comparable to being seven years younger. That’s why we will make sure to continue our studies of how green space development impacts people,’ added Vasily Klucharev.
See also:
HSE University and Adyghe State University Launch Digital Ethnolook International Contest
The HSE Centre for Language and Brain and the Laboratory of Experimental Linguistics at Adyghe State University (ASU) have launched the first Digital Ethnolook International Contest in the Brain Art / ScienceArt / EtnoArt format. Submissions are accepted until May 25, 2024.
Parietal Cortex Influences Risk-Taking Behaviour
Making decisions in situations involving risk and uncertainty is an inherent aspect of our daily lives. Should I obtain luggage insurance for my flight, cross the road when the light is red, or leave my current job for a new opportunity? Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience conducted an experiment to clarify the role the parietal cortex plays in decision-making in the context of risk. They found that suppression of activity in the parietal cortex resulted in subjects being less inclined to take risks. A paper with the study findings has been published in Cerebral Cortex.
Cognitive Reappraisal of Negative Emotions Can Help Manage Stress
Researchers at the HSE International Laboratory of Social Neurobiology assessed the effectiveness of two strategies for regulating emotions: reappraisal and suppression. Having analysed data on the electrical activity of 60 individuals’ brains, the scientists discovered that both approaches put additional strain on the nervous system. It was also found that individuals who are prone to emotional contagion tend to be more effective in using reappraisal and managing negative emotions. The paper has been published in Experimental Brain Research.
Russian Researchers Unveil Mechanism Underlying Language Processing Disruptions in Epilepsy Patients
Researchers at HSE University and the Pirogov National Medical and Surgical Centre have examined alterations induced by epilepsy in the language-related neural network within the brain. Using graph-based analysis, the researchers studied fMRI data from 28 patients and found that in epilepsy, both hemispheres of the brain become activated during language processing and short connections form between the hemispheres, while long connections within one hemisphere are disrupted. The study has been published in Epilepsy&Behavior.
Researchers at HSE University Identify the Most Walkable Areas in Moscow
Experts at HSE University and Lomonosov Moscow State University examined the available data on Moscow's walkability and found the central and south-western parts of the city to be more walkable than others. However, the eastern and south-eastern areas are in need of improvements to make them more pedestrian-friendly. The study has been published in Cities.
HSE Creates ‘Transfer of Neurocognitive Technologies’ Consortium
HSE, the Pirogov National Medical and Surgical Centre, and the Centre for Speech Pathology and Neurorehabilitation of the Moscow Healthcare Department have signed an agreement on cooperation and the creation of a ‘neuro-consortium’ under the name ‘Transfer of Neurocognitive Technologies’. The new body will boost the development and implementation of advanced solutions in neurotechnology aimed at maintaining and improving people's health. The agreement was signed for five years, and the consortium is open to new participants.
HSE University Urban Planners Take Part in Global Mayors’ Forum in Guangzhou, China
A team from HSE University's Faculty of Urban and Regional Development took part in the Global Mayor’s Forum—a global event in urban development. Held in December 2023 in Guangzhou (PRC), the largest congress of urban planners brought together more than 800 guests from 65 cities and 37 countries, as well as nine international organisations.
'While it May Sound Futuristic, It Holds Great Promise': Olga Dragoy Shares Her Thoughts on Language Function Restoration and the Future of Neurotechnology
In the spring of 2023, the fifth strategic project of the Priority 2030 programme, 'Human Brain Resilience: Neurocognitive Technologies for Adaptation, Learning, Development and Rehabilitation in a Changing Environment,' was launched at HSE University. The strategic project brings together researchers from all campuses of HSE University. In her interview with the HSE News Service, Olga Dragoy, head of the strategic project and Director of the HSE Centre for Language and Brain, shares an overview of the advanced technologies neuroscientists are creating today, the underlying inspiration driving these efforts, and the operational dynamics of interdisciplinary applied projects.
‘It Was Great to Look at Scientific Achievements through the Eyes of a Journalist, not a Scientist’
HSE University in Nizhny recently hosted the 2nd Autumn Neuro-linguistic School ‘NeuroSciCom: Popularising Language and Brain Studies’ for scientists and students at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain Studies in Nizhny Novgorod. The school was held as part of the 'Human Brain Resilience: Neurocognitive Technologies for Adaptation, Learning, Development and Rehabilitation in a Changing Environment' Strategic Project of the Priority 2030 programme.
The Brain Is a Network of Networks. Scientists Have Found a Way to Unravel Them
A team of researchers from HSE University and the Artificial Intelligence Research Institute (AIRI) have demonstrated the effectiveness of the PSIICOS method they had previously developed for non-invasive mapping the neural networks in the brain based on its electrical activity. Unlike other methods, it does not search for individual neuronal sources to be then combined into networks but instead looks directly for the functional networks of interconnected neuronal populations—and does so swiftly and accurately. The study findings have been published in NeuroImage.