Moscow and St Petersburg Rank among Global Leaders in Spatial and Technological Development
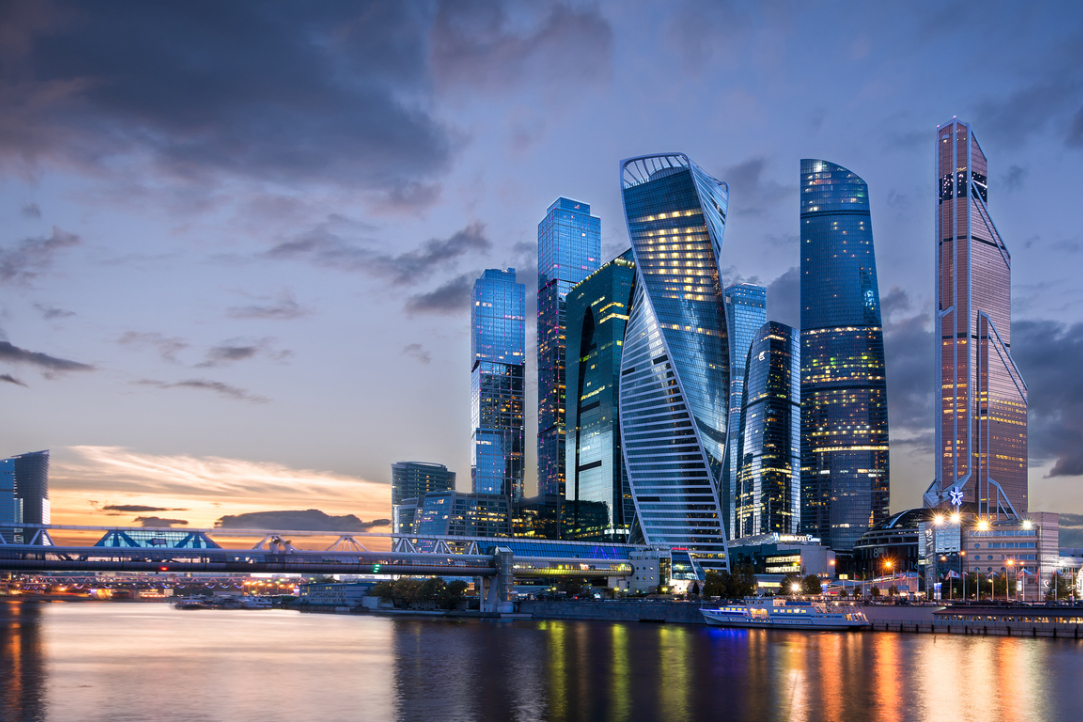

HSE experts, in collaboration with researchers from China and India, have participated in the development of the Urban & Innovation Environment Index, a global ranking of cities. Moscow ranks fifth in the final global rating of urban agglomerations and first in the rating for those in BRICS+ countries. St Petersburg ranks seventh in the global rating and third in the BRICS+ rating.
A consortium of academic institutions from China, India, and Russia has published the Urban & Innovation Environment Index, a global ranking of urban agglomerations in terms of their technological and spatial development. The consortium members include South China University of Technology, Guangzhou Academy of Social Sciences, the HSE Faculty of Urban and Regional Development (in partnership with the Geodata Centre of the HSE Faculty of Geography and Geoinformation Technology), and O.P. Jindal Global University.
Moscow ranks fifth in the final rating of urban agglomerations and first in the rating of BRICS+ countries' agglomerations. St Petersburg ranks seventh in the final rating and third in the BRICS+ rating. The world's 100 largest agglomerations were analysed, of which 30 were selected for the final rating. The full version of the index is available at the project's website.


Evgeny Mikhaylenko, Director, CITY Centre; Dean, Faculty of Urban and Regional Development, HSE University:
'Moscow rightfully stands as one of the most comfortable and modern megacities worldwide. Each year, large-scale changes are implemented in the capital to enhance the comfort and quality of life of its residents: cultural centres, schools and clinics are increasingly accessible and conveniently located, while Moscow's urban transportation network undergoes continuous modernisation and expansion. The city is actively advancing its digital services and enhancing district connectivity, factors that have significantly contributed to its index rating. Surpassing Shanghai, New York, Beijing, and Tokyo, the Russian capital's high position in the ranking would have been unattainable without continuous qualitative improvements in the urban environment.'
The index measures the physical accessibility of urban services for residents, highlighting how a well-balanced spatial structure and the integration of innovation into the local economy enable each citizen to save valuable time, which is essential in today's fast-paced lifestyle. The index considers various parameters of urban development, making it possible to identify strengths, areas of concern, and priorities for urban policy. This data is valuable to authorities at various levels, assisting them not only in the development of the city but also in the implementation of central government programmes.
The index is a pioneering tool that facilitates a comprehensive assessment of a city's environment by considering time-saving measures and intra-urban differentiation. It takes into account the interplay between spatial, innovative, and technological factors of development. Online services that make citizens' lives more comfortable and goods more accessible require the presence of a readily available physical infrastructure of sufficient quality. Ordering a taxi to a location is impossible without a proper road for access; a marketplace becomes inconvenient if its pick-up point is hard to reach, and the distance to restaurants and dark stores directly impacts the promptness of food and grocery deliveries.
The indicators used in the index are based on open-access statistical and spatial data, including satellite images and the results of their processing
The boundaries of agglomerations for the study were determined using a multi-criteria spatial analysis method based on data reflecting the distribution of population density, housing development, and transport accessibility
The methodology behind the index makes it possible to take into account residents' diverse needs, which may vary depending on lifestyle, marital status, and income level.
The final rating is based on a set of indicators grouped into two main categories.
Spatial Development Group of Indicators:
level of polycentricity
functional diversity of suburbs
integration of the road network and public transport infrastructure
diversity of urban morphology types
accessibility of green spaces
Technological Development Group of Indicators:
development of sharing, taxi, and delivery services
development of government public services
scientific and cultural potential

Ruslan Goncharov, Associate Professor, Head of the Vysokovsky Graduate School of Urbanism, Faculty of Urban and Regional Development, HSE University:
'In a modern city, available time is an essential resource. Therefore, a city's appeal to residents is determined by the extent to which it facilitates time saving through well-developed digital services and easily accessible physical infrastructure. The idea of taking a fresh look at urban development has been a recurring theme in expert discussions for quite some time. That is why we responded with great enthusiasm to the proposal from our international colleagues to join in the study. We hope that its results will encourage a somewhat different perspective on goal setting in urban development.'

Russian cities rank at the top on several indicators:
The project team notes the high level of public transport development: Moscow and St Petersburg rank among the five global leaders, surpassing Seoul, Tokyo, and Beijing
Moscow ranks fourth globally in terms of scientific potential, after Tokyo, London, and Seoul
Moscow leads and St Petersburg ranks in the top three agglomerations in terms of functional diversity of suburbs
St Petersburg is recognised as the most polycentric city globally, while Moscow ranks sixth in terms of polycentricity, after Paris, Milan, London, and Tehran
In terms of cultural potential, Moscow and St Petersburg rank in the top five, ahead of London and New York, among others
Accessibility of green areas is also high in the two Russian capitals, with both ranking in the top ten

Kirill Puzanov, Associate Professor, Vysokovsky Graduate School of Urbanism, Faculty of Urban and Regional Development; Scientific Supervisor, Master's Programme 'Digital Urban Analytics', HSE University:
'An important methodological novelty of the index is a partial shift from relying on statistical data to placing greater emphasis on spatial differentiation. By relying solely on citywide averages, as is common in many international studies, we fail to capture the spatial metric of the city, leading to equal distribution of all indicators across all residents. But this approach is akin to calculating "the average temperature in a hospital," whereas when considering the world's major cities, let alone urban agglomerations, we all understand that significant imbalances exist in their spatial and technological development. These imbalances are relevant to our index, and they affect the final ranking of each city.'
See also:
Faculty of Urban and Regional Development Develops a Draft of a New Transport Scheme of Obninsk
On May 3rd, a briefing and presentation session of a project for the development of the city's transport scheme took place in the Obninsk administration. This large-scale project has been implemented by staff from the Institute of Transport Economics and Transport Policy Studies of the HSE Faculty of Urban and Regional Development.
What Makes Cities Attractive to Innovators?
How do we evaluate the contribution of innovations to urban development? Why do cities need innovation? How do cities attract top talents? These and many other questions were addressed by the participants of the international online discussion ‘Increasing the Innovation Attractiveness of Global Cities: Best Practices’ organised by the HSE Institute for Statistical Studies and Economics of Knowledge (HSE ISSEK) on March 1, 2023. The event also featured the presentation of new outcomes of a global study on urban innovation carried out since 2020.
Card Index: City as a Palimpsest
Any cultural landscape is a narrative or a story. A big, modern city with its multiple contesting meanings and social practices, an ongoing dialogue of different eras, and physical spaces coexisting with imaginary ones can be compared to a complex, multi-layered text. A recent paper by Ivan Mitin, Associate Professor in the Faculty of Urban and Regional Development, portrays the big city as an enormous, continuously updated manuscript.
Consortium Led by HSE University Wins Norilsk Renovation Competition
The Open International Architectural and Planning Concept Competition for the Renovation of Norilsk up to 2035 received a total of 27 submissions from 12 individual applicants and 15 consortiums from 13 countries. The winner was a consortium of six companies from Russia, Austria, and France led by HSE University. Eleven HSE University institutes and competency centres were involved in the development of the project. The aim of the competition was to create a comprehensive vision of the development of Norilsk up to 2035.
HSE Relaunches Webinar Series ‘Megacities of the Future 2:0. New Challenges’
HSE University is pleased to announce the relaunch of its popular webinar series, Megacities of the future 2:0. New Challenges. The series focuses on issuesof modern urban development and is team taught by HSE University professors and lecturers from different faculties. The webinars consider urban developmental issues through the lenses of a range of fields, including Arts and Design, Computer Science, Electronics, Mathematics and Communication Systems, Economics and Management, Urban Studies, and Russian Studies.
Exploring Growth Patterns in Russia’s Largest Cities
Robert Buckley, a senior fellow in the Graduate Program in International Affairs at The New School in New York City, works largely on issues relating to urbanization in developing countries. At the upcoming XIX April International Academic Conference on Economic and Social Development, he will be participating a roundtable on Urbanization and Economic Development during which he will give a presentation entitled ‘The Morphology of Large Russian Cities: Patterns and Conjectures’.
HSE’s Projects for the City
Staff from the Design Laboratory (the design wing of the HSE School of Design) teamed up with design students to carry out an extensive study on the territorial branding of Moscow’s various districts. In addition, undergraduate and graduate students of HSE MIEM developed ‘smart systems’ for monitoring urban space and managing energy consumption and lighting systems. The projects were presented to Moscow Mayor Sergey Sobyanin during his most recent visit to the Higher School of Economics.