Researchers Compare Energy Consumption During Extraction and Synthesis of One Diamond Carat

Researchers from HSE University, RAS, and Skoltech have compared actual specific energy consumption in the production of diamonds using traditional (mining) and innovative (synthesis) methods. Depending on the technology, 36 to 215 kWh of energy is consumed to produce a 1 carat diamond. It turned out that not all diamond synthesis technologies surpass extraction methods in terms of energy efficiency. The results of the study were published in the journal Energies.
Energy consumption in the production of diamonds serves as an indicator of overall production efficiency: the less energy is consumed, the less direct and indirect specific environmental burden the process brings about.
Energy costs are one of the main burdens in diamond production. Diamond mining in Eastern Siberia and South Africa, the ones analysed in the paper, does not go beyond the range of 96-150 kWh per carat, which roughly corresponds to the median energy efficiency.
Researchers from HSE University, the Institute of Oil and Gas Problems of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences and Skoltech analysed specific energy consumption data for diamond production. It was based on reports provided by the leading diamond producers — Alrosa and De Beers — as well as on the data taken from laboratory studies of synthesis processes.

Dr. Vladislav Zhdanov, HSE Professor and the article’s author
‘Thanks to the up-to-date data, we were able to observe the overall dynamics, which is a reduction in energy consumption. At the same time, the hypothesis that the synthesis of diamonds is priori a less environmentally burdensome means of producing diamonds has not been confirmed – at the very least, diamond mining rivals the widespread technology of chemical vapor deposition (CVD) in terms of energy efficiency.’
The researchers assume that, depending on the technology, 36 to 215 kWh of energy must be consumed in order to produce a 1 carat diamond. When synthesizing diamonds by the means of the High-Pressure-High-Temperature method (with an open cooling circuit), the most common one today, energy consumption amounts to only about 30 kWh per carat, while, when synthesizing diamonds by chemical vapor deposition, electricity consumption can exceed 200 kWh.

In other words, the energy appetites of diamond synthesis methods differ significantly. At the same time, the method of chemical vapor deposition, despite its high specific energy intensity, allows one to obtain diamonds with special properties, which are particularly useful in quantum physics and thermonuclear energy.
‘In addition to the two above-mentioned synthesis technologies, there are at least two other methods of obtaining diamonds in laboratory conditions - detonation and cavitation, the specific energy consumption of which was not considered in our study,’ says Professor Zhdanov. ‘If we try to determine the favourites in the race of synthesis technologies, then my bet is on chemical vapor deposition and cavitation. I believe that these technologies have the maximum potential.’
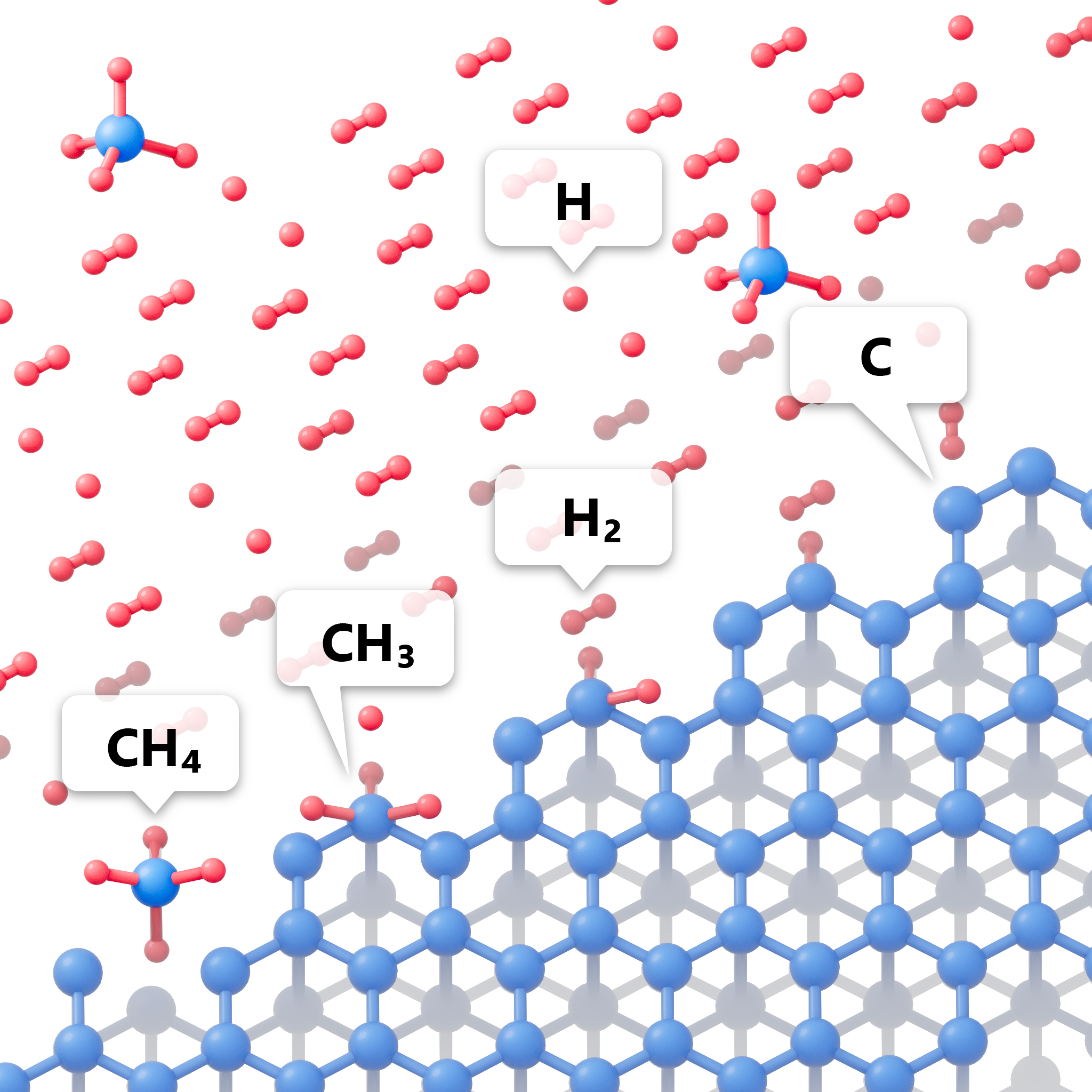
The researchers believe that both methods of diamond production, mining and synthesis, have significant potential to increase their energy efficiency, which will ultimately have positive impact on the whole industry.
The results of the study can be of significant use to both diamond producers and those end users who are interested in the environmental footprint of the products they purchase.
Vladislav Zhdanov
Professor, School of Philosophy and Cultural Studies
See also:
Physicists Propose New Mechanism to Enhance Superconductivity with 'Quantum Glue'
A team of researchers, including scientists from HSE MIEM, has demonstrated that defects in a material can enhance, rather than hinder, superconductivity. This occurs through interaction between defective and cleaner regions, which creates a 'quantum glue'—a uniform component that binds distinct superconducting regions into a single network. Calculations confirm that this mechanism could aid in developing superconductors that operate at higher temperatures. The study has been published in Communications Physics.
'Even among Geniuses, Luck Plays a Role in Winning a Nobel Prize'
Denis Bodrov studies particle physics and works at one of the four electron–positron colliders in the world. In this interview with the HSE Young Scientists project, he talks about his efforts to go beyond the Standard Model, discusses tau leptons, and shares his affection for Moscow.
Physicists at HSE University Reveal How Vortices Behave in Two-Dimensional Turbulence
Researchers from the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the HSE University's Faculty of Physics have discovered how external forces affect the behaviour of turbulent flows. The scientists showed that even a small external torque can stabilise the system and extend the lifetime of large vortices. These findings may improve the accuracy of models of atmospheric and oceanic circulation. The paper has been published in Physics of Fluids.
New Method for Describing Graphene Simplifies Analysis of Nanomaterials
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has proposed a new mathematical method to analyse the structure of graphene. The scientists demonstrated that the characteristics of a graphene lattice can be represented using a three-step random walk model of a particle. This approach allows the lattice to be described more quickly and without cumbersome calculations. The study has been published in Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical.
‘It Was Interesting to See How Our Chinese Colleagues Work’: HSE Researchers Take Part in Hefei Summer School
This summer, Diana Sukhoverkhova, Daria Mazur, and David Kagramanyan, research assistants at the MIEM HSE Laboratory for Computational Physics, spent five weeks in China. At the Future Scientist Exchange Program (FuSEP) summer school in Hefei, they worked in new fields of science together with their Chinese colleagues. HSE's promising scientists spoke to the HSE News Service about their intense and productive time in China.
‘The Fundamental Principle of Scientific Knowledge Is Honesty’
Daria Mazur has wanted to pursue science since she was 13 years old—ever since she discovered in the seventh grade that she was good at physics. In an interview for the HSE Young Scientists project, she spoke about her theoretical research on the electric double layer, speed reading, and the MGMT song ‘Little Dark Age.’
Russian Scientists Reconstruct Dynamics of Brain Neuron Model Using Neural Network
Researchers from HSE University in Nizhny Novgorod have shown that a neural network can reconstruct the dynamics of a brain neuron model using just a single set of measurements, such as recordings of its electrical activity. The developed neural network was trained to reconstruct the system's full dynamics and predict its behaviour under changing conditions. This method enables the investigation of complex biological processes, even when not all necessary measurements are available. The study has been published in Chaos, Solitons & Fractals.
Russian Physicists Discover Method to Increase Number of Atoms in Quantum Sensors
Physicists from the Institute of Spectroscopy of the Russian Academy of Sciences and HSE University have successfully trapped rubidium-87 atoms for over four seconds. Their method can help improve the accuracy of quantum sensors, where both the number of trapped atoms and the trapping time are crucial. Such quantum systems are used to study dark matter, refine navigation systems, and aid in mineral exploration. The study findings have been published in the Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics Letters.
Russian Scientists Demonstrate How Disorder Contributes to Emergence of Unusual Superconductivity
Researchers at HSE University and MIPT have investigated how the composition of electrons in a superconductor influences the emergence of intertype superconductivity—a unique state in which superconductors display unusual properties. It was previously believed that intertype superconductivity occurs only in materials with minimal impurities. However, the scientists discovered that the region of intertype superconductivity not only persists but can also expand in materials with a high concentration of impurities and defects. In the future, these superconductors could contribute to the development of highly sensitive sensors and detectors. The study has been published in Frontiers of Physics.
Scientists at HSE University Devise More Accurate Method for Predicting the Electrical Conductivity of Electrolyte Solutions
Researchers at HSE MIEM have developed a model for calculating the electrical conductivity of aqueous electrolyte solutions; for the first time, it considers the spatial distribution of ion charges instead of assuming their localisation at a single point. The model remains effective even at high electrolyte concentrations and across a wide temperature range. This breakthrough will contribute to the development of more efficient batteries and enable the calculation of electrical conductivity without the need for experimental testing. The study has been published in the Journal of Chemical Physics.